Notice
Recent Posts
Recent Comments
Link
bdfgdfg
연결리스트 - 원형, 양방향(이중) 5장 본문
반응형
원형 연결리스트
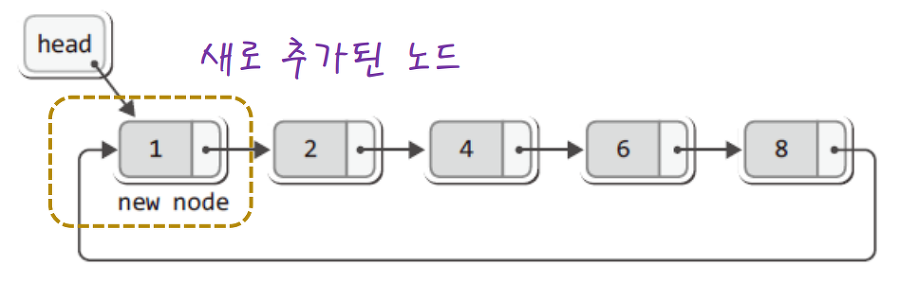
원형 연결리스트는 기존의 연결리스트에서 맨 마지막 노드가 첫 번째 노드를 가리키는 형태를 이루는게 원형 연결리스트.
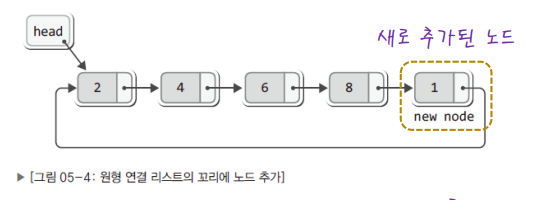
원형 연결리스트는 꼬리(마지막노드)포인터 변수가 따로 없더라도 맨 마지막에 노드를 추가할 수 있다.
다만 헤드보단 꼬리 포인터변수를 통해 원형 연결리스트를 구현하는것이 훨씬 간단하다.
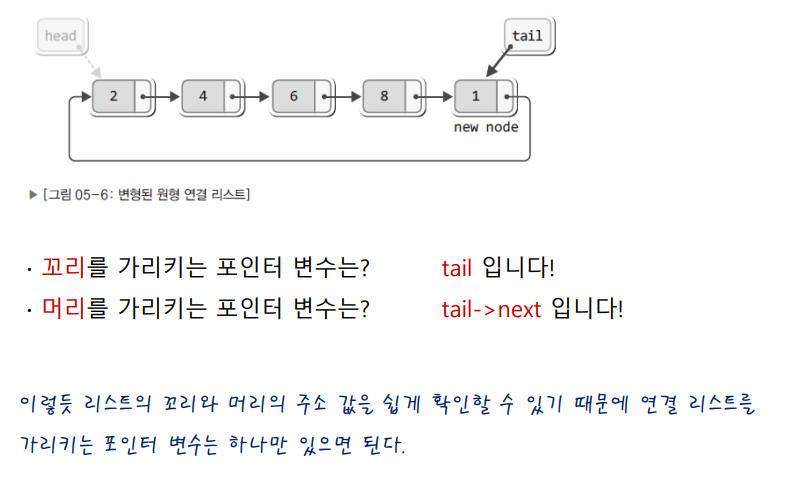
앞서 단순 연결리스트를 구현할때 변경되는것은 앞(머리) 뒤(꼬리)쪽에도 추가할 수 있게 기능을 추가하고 탐색의 경우 원형으로 계속 돌 수 있는 형태이니 다음 노드의 nullptr을 저장하지 않게만 하면 된다.
양방향 연결리스트
단순 연결리스트는 노드가 내 다음에 존재하는 노드만을 가리켰다면
양방향 연결리스트는 내 다음 노드뿐만 아니라 내 이전의 노드도 가리킨다. (노드 클래스에 포인터변수 한개 더 추가)
양방향 연결리스트의 이론은 이게 전부이고, 실제 STL list컨테이너는 양방향 연결리스트로 구현이 되어있다.
양방향 연결리스트의 간단한 코드 예시를 작성해본다.
#pragma once
class Node // int 형 데이터를 담는 노드.
{
public:
Node();
Node(int data);
~Node() = default;
int GetData() const;
void SetData(int item);
Node* GetNextNode() const;
Node* GetPrevNode() const;
void SetPrevNode(Node* prev);
void SetNextNode(Node* next);
private:
int m_data;
Node* m_prev;
Node* m_next;
};
class LinkedList
{
public:
LinkedList();
~LinkedList();
void push_front(int item);
int GetlistSize() const;
void pop_front();
bool LFirst();
bool LNext();
bool LPrevious();
Node* iterator() const;
int pop_cur();
private:
Node* m_head;
//Node* m_tail; 꼬리 삭제
Node* m_cur;
int m_size;
};
단순한 연결리스트가 다음쪽 노드만 가리켰다면 양방향 연결리스트는 이전 노드를 추가로 기억하면 된다.
cpp코드
#include "LinkedList.h"
Node::Node() : m_data(0), m_next(nullptr), m_prev(nullptr)
{
}
Node::Node(int data) : m_data(data), m_next(nullptr),m_prev(nullptr)
{
}
int Node::GetData() const
{
return this->m_data;
}
void Node::SetData(int item)
{
this->m_data = item;
}
Node* Node::GetNextNode() const
{
return this->m_next;
}
Node* Node::GetPrevNode() const
{
return this->m_prev;
}
void Node::SetNextNode(Node* next)
{
if (this == nullptr)
return;
this->m_next = next;
}
void Node::SetPrevNode(Node* prev)
{
if (this == nullptr)
return;
this->m_prev = prev;
}
LinkedList::LinkedList() : m_head(new Node()),m_cur(m_head),m_size(0)
{
}
LinkedList::~LinkedList()
{
for (int i = 0; i < m_size; ++i)
pop_front();
delete m_head; // 더미노드삭제
}
void LinkedList::push_front(int item)
{
if (this->m_head->GetNextNode() == nullptr) //노드없을때.
{
Node* newNode = new Node(item);
newNode->SetNextNode(this->m_head->GetNextNode());
newNode->SetPrevNode(this->m_head);
this->m_head->SetNextNode(newNode);
}
else //노드가 하나이상 존재할때.
{
Node* newNode = new Node(item);
Node* firstNode = this->m_head->GetNextNode();
firstNode->SetPrevNode(newNode);
newNode->SetNextNode(this->m_head->GetNextNode());
newNode->SetPrevNode(this->m_head);
this->m_head->SetNextNode(newNode);
}
++(this->m_size);
}
int LinkedList::GetlistSize() const
{
return this->m_size;
}
void LinkedList::pop_front()
{
if (this->m_size <= 0)
return;
Node* popNode = this->m_head->GetNextNode();
Node* popNextNode = popNode->GetNextNode();
popNextNode->SetPrevNode(this->m_head);
this->m_head->SetNextNode(popNextNode);
int data = popNode->GetData();
--(this->m_size);
delete popNode;
}
int LinkedList::pop_cur()
{
if (this->m_size <= 0)
return 0;
Node* prevNode = this->m_cur->GetPrevNode();
Node* nextNode = this->m_cur->GetNextNode();
Node* delNode = this->m_cur;
int data = delNode->GetData();
prevNode->SetNextNode(delNode->GetNextNode());
nextNode->SetPrevNode(delNode->GetPrevNode());
--this->m_size;
delete delNode;
return data;
}
bool LinkedList::LFirst()
{
if (this->m_size <= 0)
return false;
this->m_cur = this->m_head->GetNextNode();
return true;
}
bool LinkedList::LNext()
{
if (this->m_cur->GetNextNode() == nullptr)
return false;
this->m_cur = this->m_cur->GetNextNode();
return true;
}
Node* LinkedList::iterator() const
{
return this->m_cur;
}
bool LinkedList::LPrevious()
{
if (this->m_cur->GetPrevNode() == nullptr)
return false;
this->m_cur = this->m_cur->GetPrevNode();
return true;
}
반응형
'CS > 자료구조 알고리즘' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 큐(Queue)와 덱(Deque) - 7장 (0) | 2021.07.03 |
|---|---|
| 스택 - 6장 (0) | 2021.07.03 |
| 연결리스트 - 3장,4장 (0) | 2021.07.03 |
| 재귀함수 - 2장 (1) | 2021.07.02 |
| 알고리즘의 성능분석 방법 - 1장 (0) | 2021.07.02 |
Comments




